24、Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。
你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
24-1
Example:
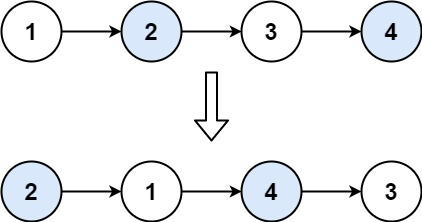
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
题解
1、双指针,两个反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
fast = fast->next;
if (fast == nullptr) { // 链表只有一个节点
return head;
}
ListNode dummy(0);
dummy.next = head->next;// 新的头节点
ListNode* pre = nullptr;// 记录前一个节点
while (fast != nullptr) {
ListNode* t = fast->next;// 1 临时记录
fast->next = slow; // 2 快慢反转
slow->next = t;// 3 快慢反转
if (pre == nullptr){ // 第一次更新前节点
pre = slow; // 4 更新前节点
} else {
pre->next = fast;// 4.1 连接起来
pre = slow;// 4.2 更新前节点
}
if (t != nullptr) {
slow = t;// 5
}else {
break;
}
if (t->next != nullptr){
fast = t->next;// 6
} else {
break;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
// 他人的简约版
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head){
ListNode * dummy(0);
ListNode pre = &dummy;
dummy.next = head;
ListNode * cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;// 辅助节点
if (next == nullptr) { break;}// 只剩一个节点了
pre->next = next; // 第二个指针获得前序节点的引用
cur->next = next->next;// 第一个指针引用第三个节点
next->next = cur;// 第二个节点引用第一个节点
pre = cur;// 更新前序节点
cur = cur->next;// 更新下一个的第一个节点
}
return dummy.next;
}
Java代码
要牢记每个节点有两个属性:一个是值,一个是next指针,混淆了。
// 递归版
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// 临时存储下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
// 第一个节点指向后续的节点对的第一个节点
head.next = swapPairs(next.next);
// 第二个节点变成第一个节点
next.next = head;
// 返回新的第一个节点
return next;
}
// 非递归版
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
pre.next = head;
ListNode temp = pre;
while(temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {
ListNode start = temp.next;// 第一个节点
ListNode end = temp.next.next;// 第二个节点
temp.next = end;// 头结点指向第二个节点
start.next = end.next;// 第一个节点指向第三个节点
end.next = start;// 第二个节点指向第一个节点
temp = start;// 更新下一组节点的前一个节点
}
return pre.next;
}
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/hua-jie-suan-fa-24-liang-liang-jiao-huan-lian-biao/
25、Reverse Nodes in K-Group
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
Example:
Given this linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
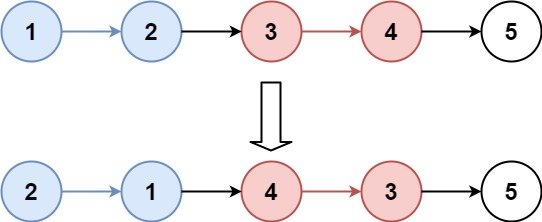
For k = 2, you should return: 2->1->4->3->5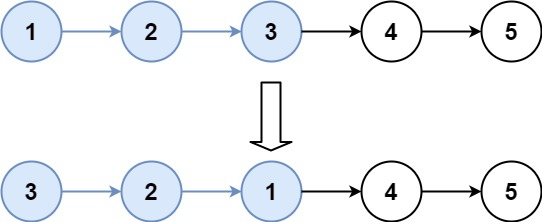
For k = 3, you should return: 3->2->1->4->5
Note:
- Only constant extra memory is allowed.
- You may not alter the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
题解
1、递归分段反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 递归分段遍历
ListNode* reverseKGroupCore(ListNode* head, int k, int times){
if (times == 0) return head;
ListNode nHead(0);// 辅助头节点
nHead.next = head;// 当前的头节点
int i = 0; // 循环辅助
ListNode* q = head->next;
while(i < k-1) {
ListNode* t = q->next; // 1 弟弟先站一边
q->next = nHead.next; // 2 哥哥准备上位
nHead.next = q; // 3 哥哥正式上位
q = t; // 4 弟弟晋升为哥哥
i++;// 循环+1
}
// 递归分段反转链表
head->next = reverseKGroupCore(q,k,times-1);
return nHead.next; // 返回反转后的新的段头节点
}
// 头插法反转k个节点组成的单元
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
int len = 0;
ListNode* p = head;
while (p != nullptr) {// 统计链表长度
len++;
p = p->next;
}
if (len < k) {// 长度小于k,不用反转
return head;
} else {
return reverseKGroupCore(head,k,len/k);
}
}
};
// 其他小伙伴实现的递归
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* pre=head;
int count=0;
while(pre!=NULL&&count<k){
pre=pre->next;
count++;
} //退出循环后pre指向第k+1个节点
if(count==k) {
pre=reverseKGroup(pre,k);
while(count>0){
/* head指向本次循环反转指向的节点
temp指向下次循环反转指向的节点
*/
ListNode* temp=head->next;
head->next=pre;
pre=head;
head=temp;
count--;
}
head=pre;
}
return head;
}
};
// 作者:carryzz
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/c-liang-chong-jie-fa-bian-li-di-gui-dai-xiang-xi-z/
Java 递归版——其他小伙伴的
- 利用数组去反转k个节点
- 空间复杂度太大O(n)
属实是使用数组来操作链表,真的是bug般的存在!!!
- 初始化链表节点数组
- 遍历k个节点,从后往前加入到数组中
- 不足k个直接return,因为此时还没有有翻转,不影响。
- 遍历数组,一次翻转指针引用
- 递归遍历k个节点并反转
- 返回数组的最后个节点作为头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
int tempK = k;// 暂存
ListNode[] stack = new ListNode[k];// k组列表
ListNode q = head;
while(k > 0) { // 把当前k个结点存入栈中 k--
stack[tempK - k] = q;
if (q != null) {
q = q.next;
} else {
return head;
}//结点凑不到k个时,直接返回原部分链表。
k--;
}
// 翻转当前k个节点k++
while(k < tempK - 1) {
k++;
stack[tempK - k].next = stack[tempK - k - 1];
}
// 递归处理
stack[0].next = reverseKGroup(q, k + 1);
return stack[tempK - 1];
}
}
// 作者:rulcy_daily_code
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/xie-yi-ge-wan-wan-by-rulcy_daily_code/
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1056615746@qq.com

