37、解数独
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
- Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
- Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
- Each of the the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character '.' .
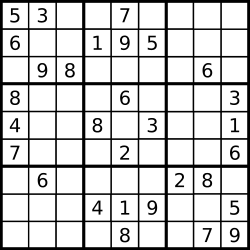
- 一个解
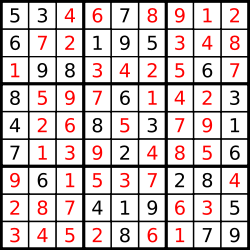
…and its solution numbers marked in red.
Note:
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
- The given board size is always
9x9.
解题思路——回溯法
1⃣️如何枚举全部情况?
- 方块索引 = (r / 3) * 3 + c / 3
- / 为整数除法
算法描述
- 回溯函数backtrack(r, c)
- 从
r = 0, c = 0开始,遍历每一个空的方格进行枚举 d = 1~9,放入(r, c)处- 如果 d 满足当前约束的条件,
- 将d放入 (r,c) 里
- 记录 d 已经处现的行、列和块
- 如果 r = 8 && c = 8
- 结束找到解
- 否则,继续解决下一个空格
- 如果,出现了矛盾,进行回溯,移除 (r,c),最后填的数字
- 如果 d 满足当前约束的条件,
class Solution {
// box size
int n = 3;
// row size
int N = n * n;
int [][] rows = new int[N][N + 1];// 统计每一行的数字
int [][] columns = new int[N][N + 1];// 统计每一列的数字
int [][] boxes = new int[N][N + 1];// 统计每一个方块的数字
char[][] board;
boolean sudokuSolved = false;
// 判断能不能放进去
public boolean couldPlace(int d, int row, int col) {
int idx = (row / n ) * n + col / n;
return rows[row][d] + columns[col][d] + boxes[idx][d] == 0;
}
// 将数字 d 放入 (r,c)里面
public void placeNumber(int d, int row, int col) {
int idx = (row / n ) * n + col / n;
rows[row][d]++;
columns[col][d]++;
boxes[idx][d]++;
board[row][col] = (char)(d + '0');
}
// 将数字 d 从 (r,c) 里面移除
public void removeNumber(int d, int row, int col) {
int idx = (row / n ) * n + col / n;
rows[row][d]--;
columns[col][d]--;
boxes[idx][d]--;
board[row][col] = '.';
}
// 放置下一个数字
public void placeNextNumbers(int row, int col) {
if ((col == N - 1) && (row == N - 1)) {// 已到达最后一个空格,结束。
sudokuSolved = true;
} else {
if (col == N - 1) backtrack(row + 1, 0);// 一行结束
else backtrack(row, col + 1);// 一行还没有结束
}
}
// 回溯主函数
public void backtrack(int row, int col) {
if (board[row][col] == '.') {
for (int d = 1; d < 10; d++) {// 1~9 枚举
if (couldPlace(d, row, col)) {// 可以放进去
placeNumber(d, row, col); // 放进去
placeNextNumbers(row, col);// 放下一个数字
// 没有找到解,进行回溯
if (!sudokuSolved) removeNumber(d, row, col);
}
}
}
else placeNextNumbers(row, col);// 直接放下一个空格
}
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
this.board = board;
// 初始化三个辅助数组
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
char num = board[i][j];
if (num != '.') {
int d = Character.getNumericValue(num);
placeNumber(d, i, j);
}
}
}
// 进行回溯求解
backtrack(0, 0);
}
}
// 作者:LeetCode
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/jie-shu-du-by-leetcode/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
一个子函数求解
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
// 三个布尔数组 表明 行, 列, 还有 3*3 的方格的数字是否被使用过
boolean[][] rowUsed = new boolean[9][10];
boolean[][] colUsed = new boolean[9][10];
boolean[][][] boxUsed = new boolean[3][3][10];
// 初始化
for(int row = 0; row < board.length; row++){
for(int col = 0; col < board[0].length; col++) {
int num = board[row][col] - '0';
if(1 <= num && num <= 9){
rowUsed[row][num] = true;
colUsed[col][num] = true;
boxUsed[row/3][col/3][num] = true;
}
}
}
// 递归尝试填充数组
recusiveSolveSudoku(board, rowUsed, colUsed, boxUsed, 0, 0);
}
private boolean recusiveSolveSudoku(char[][]board, boolean[][]rowUsed, boolean[][]colUsed, boolean[][][]boxUsed, int row, int col){
// 边界校验, 如果已经填充完成, 返回true, 表示一切结束
if(col == board[0].length){// 一行结束
col = 0;
row++;
if(row == board.length){// 一列结束
return true;
}
}
// 是空则尝试填充, 否则跳过继续尝试填充下一个位置
if(board[row][col] == '.') {
// 尝试填充1~9
for(int num = 1; num <= 9; num++){
boolean canUsed = !(rowUsed[row][num] || colUsed[col][num] || boxUsed[row/3][col/3][num]);
if(canUsed){
// 更新辅助数组
rowUsed[row][num] = true;
colUsed[col][num] = true;
boxUsed[row/3][col/3][num] = true;
// 放入数字num
board[row][col] = (char)('0' + num);
// 递归填充,找到解就退出。有点贪心的感觉
if(recusiveSolveSudoku(board, rowUsed, colUsed, boxUsed, row, col + 1)){
return true;
}
// 否则,回溯移除num
board[row][col] = '.';
rowUsed[row][num] = false;
colUsed[col][num] = false;
boxUsed[row/3][col/3][num] = false;
}
}
} else {// 不为空
return recusiveSolveSudoku(board, rowUsed, colUsed, boxUsed, row, col + 1);
}
return false;
}
}
// 作者:I_use_python
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/hui-su-fa-jie-shu-du-by-i_use_python/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
C++实现
bool solved = 0;// 回溯结束条件变量
bool row[9][10], col[9][10], box[9][10];
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
// 分配空间
memset(row, 0, sizeof(row));
memset(col, 0, sizeof(col));
memset(box, 0, sizeof(box));
// 辅助变量初始化
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') continue;
int index = i / 3 * 3 + j / 3;
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = box[index][num] = 1;
}
// 回溯递归
DFS(0, 0, board);
}
// 深度优先搜索,回溯法的本质
void DFS(int i, int j, vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if (i == 9) { solved = 1; return; } // 结束递归
if (board[i][j] != '.') {// 深度搜索
if (j < 8) DFS(i, j + 1, board);
else DFS(i + 1, 0, board);
}
else {
int index = i / 3 * 3 + j/3;
for (int num = 1; num <= 9; num++) {
if (!row[i][num] && !col[j][num] && !box[index][num]) {
// 放入数字
board[i][j] = num + '0';
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = box[index][num] = 1;
// 深度优先搜索
if (j < 8) DFS(i, j + 1, board);
else DFS(i + 1, 0, board);
// 取出数字
if (!solved) { // 还没有解决,回溯
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = box[index][num] = 0;
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
}
}
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1056615746@qq.com

