题目
给定编号从 0 到 n - 1 的 n 个结点。给定一个整数 n 和一个 edges 列表,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条无向边。
如果这些边能够形成一个合法有效的树结构,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
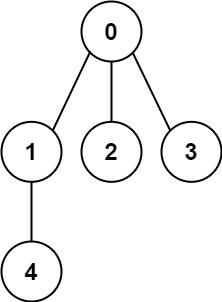
输入: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]]
输出: true
示例 2:
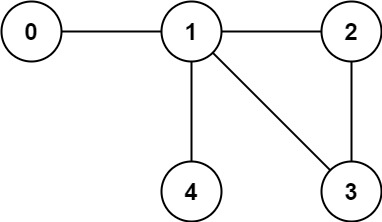
输入: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]]
输出: false
提示:
1 <= n <= 20000 <= edges.length <= 5000edges[i].length == 2- $0 <= a_i, b_i < n$
- $a_i != b_i$
- 不存在自循环或重复的边
分析
一个无向图有生成树的条件是图中无环且只有一个连通域。
并查集
并查集,如果合并的两个点在一个集合中,则这个图是有环的
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
UnionFindSet set = new UnionFindSet(n);
for (int[] edge : edges) {
if (!set.union(edge[0],edge[1])) {
return false;
}
}
return set.getCount() == 1;
}
}
// 并查集实现
class UnionFindSet {
int n = 0;
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
int count;// 统计单连通域的数量
UnionFindSet(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.count = n;
this.parent = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
this.rank = new int[n];
}
// 找到根节点
private int findRoot(int x) {
int root = x;
while(parent[root] != -1) {
root = parent[root];
}
return root;
}
// x y相连,他们的根不能相连,否则会有环
public boolean union(int x, int y) {
int xR = findRoot(x);
int yR = findRoot(y);
// 判断是否有环
if (xR == yR) return false;
// 连接起来,根的值是最大的
if (rank[xR] > rank[yR]){
parent[yR] = xR;// y连接到x
} else if (rank[xR] < rank[yR]){
parent[xR] = yR;// x连接到y
} if (rank[xR] == rank[yR]){
parent[xR] = yR;// 默认 x连接到y
rank[xR]++;// 累加 xR yR都可以
}
count--;// 新的节点可以联通,可能的单连通数量--
return true;
}
public int getCount() {
return this.count;
}
}
BFS
- 根据边构建邻接矩阵,然后进行BFS,在遍历过程中将访问过的节点涂黑,并记录访问过的节点。
- 如果有节点已经被访问过,则表示有环,如果遍历完成后还有节点没有被访问到,则表示连同分量大于1。
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
int[][] graph = new int[n][n];// 邻接矩阵
// 根据点边列表,进行初始化
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]][edge[1]] = 1;
graph[edge[1]][edge[0]] = 1;
}
// BFS 辅助队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(0);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// 实施BFS,因为初始节点是0,只能对0所在的连通域广度优先遍历
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer cur = queue.poll();
visited[cur] = true;
// 对于点cur,遍历所有其他的点,判断是否连通
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
// 如果两点相连
if (graph[cur][i] == 1) {
if (visited[i]) {
return false;// 存在环,直接返回
}
visited[i] = true;
graph[cur][i] = 0;
graph[i][cur] = 0;
queue.add(i);
}
}
}
// 保证每个点都被访问过,否则不是单连通域。
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
DFS
整体代码和BFS一样,只是因为栈和队列的元素进出方式不一致,而又广度优先和深度优先的差异。
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
int[][] graph = new int[n][n];// 邻接矩阵
// 根据点边列表,进行初始化
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]][edge[1]] = 1;
graph[edge[1]][edge[0]] = 1;
}
// DFS 辅助栈
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(0);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// 实施DFS,因为初始节点是0,只能对0所在的连通域深度优先遍历
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
Integer cur = stack.pop();
visited[cur] = true;
// 对于点cur,遍历所有其他的点,判断是否连通
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
// 如果两点相连
if (graph[cur][i] == 1) {
if (visited[i]) {
return false;// 存在环,直接返回
}
visited[i] = true;
graph[cur][i] = 0;
graph[i][cur] = 0;
stack.push(i);
}
}
}
// 保证每个点都被访问过,否则不是单连通域。
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1056615746@qq.com

