1007、 行相等的最少多米诺旋转
在一排多米诺骨牌中,tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 分别代表第 i 个多米诺骨牌的上半部分和下半部分。(一个多米诺是两个从 1 到 6 的数字同列平铺形成的 —— 该平铺的每一半上都有一个数字。)
我们可以旋转第 i 张多米诺,使得 tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 的值交换。
返回能使 tops 中所有值或者 bottoms 中所有值都相同的最小旋转次数。
如果无法做到,返回 -1.
示例 1:
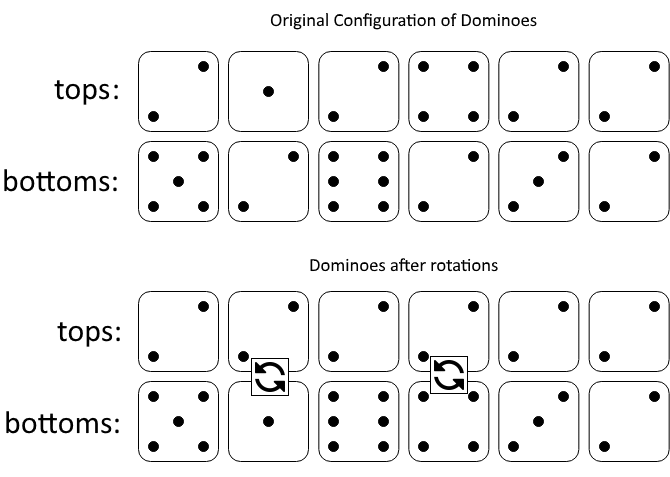
输入:tops = [2,1,2,4,2,2], bottoms = [5,2,6,2,3,2]
输出:2
解释:
图一表示:在我们旋转之前, tops 和 bottoms 给出的多米诺牌。
如果我们旋转第二个和第四个多米诺骨牌,我们可以使上面一行中的每个值都等于 2,如图二所示。
示例 2:
输入:tops = [3,5,1,2,3], bottoms = [3,6,3,3,4]
输出:-1
解释: 在这种情况下,不可能旋转多米诺牌使一行的值相等。
提示:
- 2 <= tops.length <= 2 * 104
- bottoms.length == tops.length
1 <= tops[i], bottoms[i] <= 6
分析
tops或者 bottoms 可以通过交换,变成一行所有数字都一样的数字。
方法一:暴力遍历
class Solution {
public int minDominoRotations(int[] tops, int[] bottoms) {
List<Integer> resultNumbers = new ArrayList<>();
int[] counts = new int[7];
resultNumbers.add(tops[0]);
resultNumbers.add(bottoms[0]);
// 遍历确定是否有答案,统计每次都出现的数字的出现次数
for (int i = 1;i < tops.length;i++) {
// 出现了之前没有的一组数字,返回 -1 无答案
if (!resultNumbers.contains(tops[i]) && !resultNumbers.contains(bottoms[i])) {
return -1;
}
if (resultNumbers.contains(tops[i])) {
counts[tops[i]]++;
}
if (resultNumbers.contains(bottoms[i])) {
counts[bottoms[i]]++;
}
// 移除没有出现过的数字
Iterator<Integer> iterator = resultNumbers.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer integer = iterator.next();
if (integer != tops[i] && integer != bottoms[i]) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
// 找到目标旋转的数字
int target;
if (resultNumbers.size() > 1) {
target = resultNumbers.get(0);
if (counts[target] < counts[resultNumbers.get(1)]) {
target = resultNumbers.get(resultNumbers.get(1));
}
} else {
target = resultNumbers.get(0);
}
// 统计目标数字上、下出现的次数
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0;i < tops.length;i++) {
if (tops[i] == target) {
result[0]++;
}
if (bottoms[i] == target) {
result[1]++;
}
}
// 取较小的次数
return result[0] < result[1] ? tops.length - result[1]: tops.length - result[0];
}
// 空间换时间,优化掉多余遍历
public int minDominoRotations1(int[] tops, int[] bottoms) {
List<Integer> resultNumbers = new ArrayList<>();
int[][] counts = new int[2][7];
resultNumbers.add(tops[0]);
resultNumbers.add(bottoms[0]);
counts[0][tops[0]]++;
counts[1][bottoms[0]]++;
for (int i = 1; i < tops.length; i++) {
if (!resultNumbers.contains(tops[i]) && !resultNumbers.contains(bottoms[i])) {
return -1;
}
// 无差别统计数据
counts[0][tops[i]]++;
counts[1][bottoms[i]]++;
}
int target;
if (resultNumbers.size() > 1) {
target = resultNumbers.get(0);
if (counts[0][target] < counts[0][resultNumbers.get(1)]) {
target = resultNumbers.get(resultNumbers.get(1));
}
} else {
target = resultNumbers.get(0);
}
return counts[0][target] < counts[1][target] ? tops.length - counts[1][target] : tops.length - counts[0][target];
}
}
分类讨论+模拟旋转
答案分类讨论:
- -1,不存在数字n,对于 i- tops.length, n = tops[i] or n = bottoms[i]
- tops[0] 满足要求 或者 bottoms[0]满足要求
public int minDominoRotations(int[] tops, int[] bottoms) {
// 目标要么是 tops[0] 要么是 bottoms[0]
return countTop0(tops, bottoms, tops[0]) != -1? countTop0(tops, bottoms, tops[0]) : countTop0(tops, bottoms, bottoms[0]);
}
private static int countTop0(int[] tops, int[] bottoms,int target) {
int topCount = 0;
int bottomCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tops.length; i++) {
if (tops[i] != target && bottoms[i] != target) {
return -1;
}
// 下面的翻转上来计数
if (tops[i] != target) {
topCount++;
}
// 上面翻转下去计数
if (bottoms[i] != target) {
bottomCount++;
}
}
// 取较小的值
return Math.min(topCount, bottomCount);
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 1056615746@qq.com

